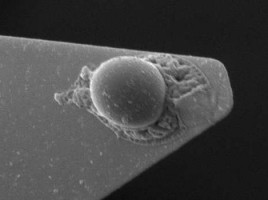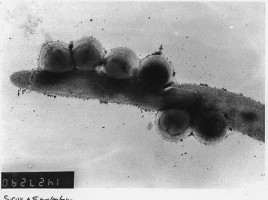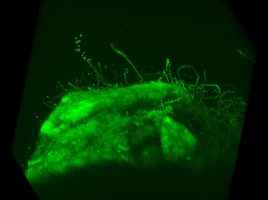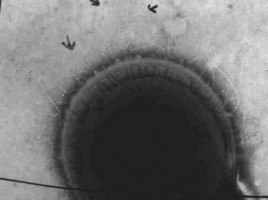
Dynamic changes in microbial community structure and function in phenol-degrading microcosms inoculated with cells from a contaminated aquifer
Contamination of aquifers by organic pollutants threatens groundwater supplies and the environment. In situ biodegradation of organic pollutants by microbial communities is important for the remediation of contaminated sites, but our understanding of the relationship between microbial development and pollutant biodegradation is poor. A particular challenge is understanding the in …