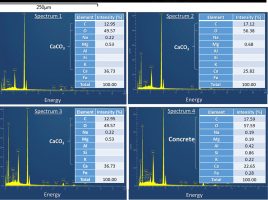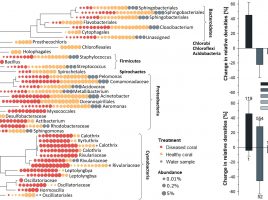
Compositional homogeneity in the pathobiome of a new, slow-spreading coral disease
Coral reefs face unprecedented declines in diversity and cover, a development largely attributed to climate change-induced bleaching and subsequent disease outbreaks. Coral-associated microbiomes may strongly influence the fitness of their hosts and alter heat tolerance and disease susceptibility of coral colonies. Here, we describe a new coral disease found in …